LLM Task
# LLM Task Node configuration
——Learn the configuration instructions of the LLM Task Node in Task Workflow through this article
# The Role of LLM Task Node
Before understanding the functions of the LLM Task Node, we hope you can learn about its scenarios and purposes:
● Function Definition: The LLM Task Node is a node used for autonomous dialogue and action calling within a Task Workflow. With a large language model (LLM) as the decision-making core, it can independently understand customer demands, collect key information, and execute cross-system actions to flexibly and dynamically achieve the goals you set.
● Application Scenarios:
- In real customer service scenarios, multi-turn dialogues often face issues such as customers suddenly changing topics, answering irrelevant questions, or incomplete expressions. These problems make it difficult for the pre-set process to respond flexibly, significantly affecting the process completion rate.
- To enhance the ability of the task flow to handle dynamic issues, we have introduced the LLM Task Node in the design. This node can conduct independent multi-turn dialogues under the guidance of pre-set steps based on task objectives and can call external tools to assist in advancing the task.
- Its core value lies in responding to customer input in real time, dynamically adjusting the execution strategy according to the dialogue progress and tool return results until the task is completed. This mechanism significantly improves the adaptability to uncertain dialogue scenarios and effectively ensures the smooth completion of complex Task Workflow.
● Compared with other nodes, the LLM Task Node has the following differences:
| Differences | LLM Task Node | Other Nodes |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario | Suitable for handling dynamic and changing dialogue scenarios. AI Agent can autonomously make decisions and adjust behavior based on customer feedback. | Suitable for scenarios where the dialogue process is stable and requires high accuracy. |
| Configuration Method | Use natural language to describe task objectives and task descriptions, which may contain complex multiple steps. | Drag and drop different nodes to design complex multi-step tasks. |
| Execution Method | The LLM autonomously decides dialogue content and invokes actions based on the task objectives and descriptions. | Strictly executes according to the backend configuration, such as pre-set scripts. |
| End Condition | Continues to push multi-turn dialogue until the task's end conditions are met. | Proceeds to the next node immediately after running finished. |
| Dialogue Experience | More human-like, with stronger comprehension capabilities | More stable, more strictly adheres to configuration |
| Exception Handling Capability | Can flexibly handle various unpredictable situations in customer service scenarios | Lacks the ability to cope with unpredictable situations |
# Scenario Examples
In the after-sales service of the smart manufacturing industry, customers often need to inquire about nearby maintenance service outlets or service stores to conduct inspection and repair of product equipment; or when inquiring about stores, they may suddenly ask other questions such as relevant warranty policies. Through the configuration of the LLM Task Node, AI Agent can independently call interfaces, assign values to variables, retrieve knowledge bases, etc., within this node.
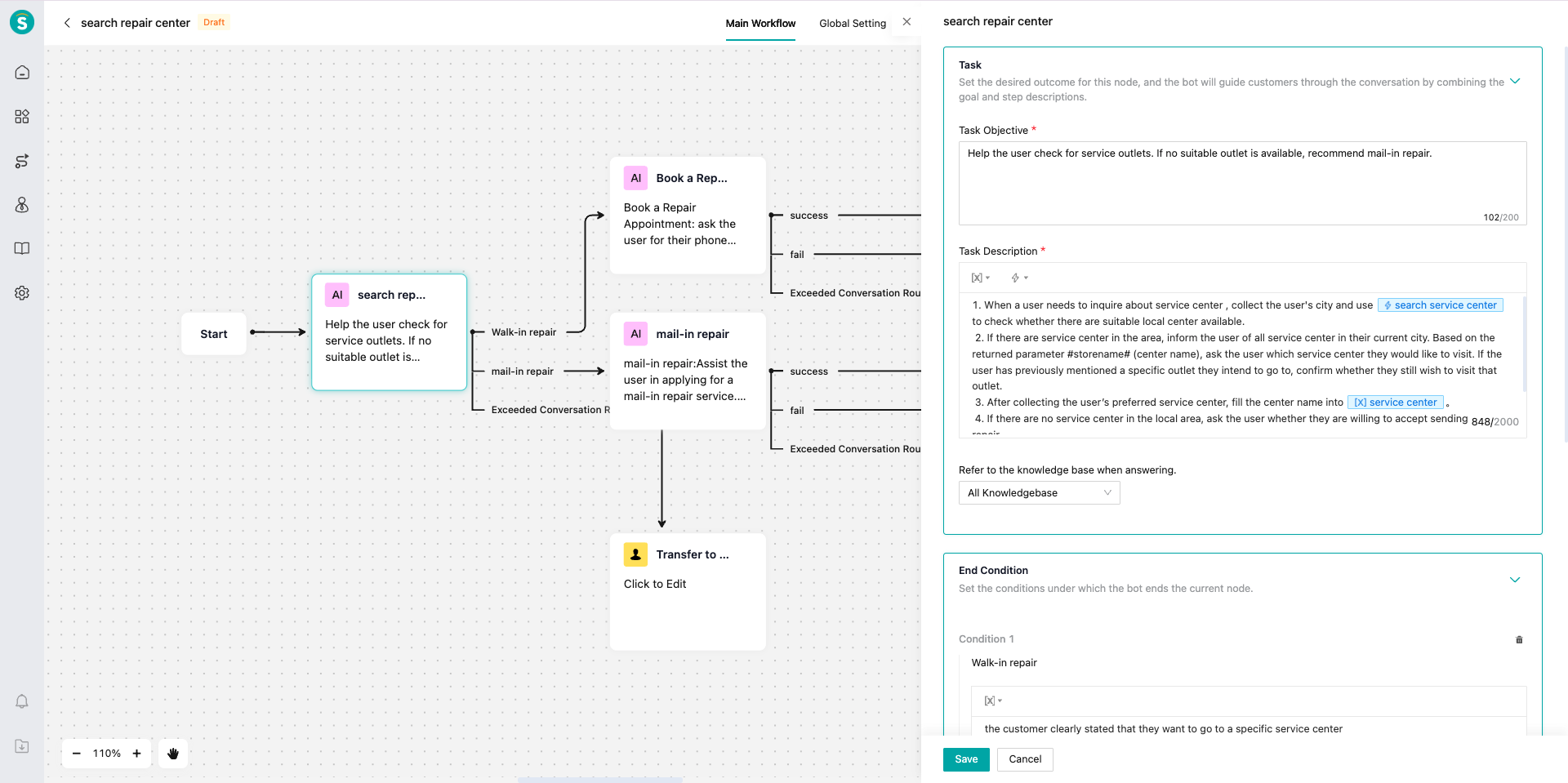
- Task Objective: Assist customers in inquiring about repair centers information.
- Task Description:
Step 1: When a user needs to inquire about repair center, collect the user's located city, and use the action 「search repair center」to check whether there are suitable repair center in the local area.
step 2. If there are local repair center, inform the user of all repair centers in the current city, and use the interface output parameter "storename" to ask the user which repair center they want to go to. If the user has previously mentioned wanting to go to one of the repair center, confirm with the user whether they want to go to the previously mentioned place.
step 3. After collecting the service outlet that the user wants to go to, populate the outlet name into the variable 「repair center」.
step 4. If there are no local repair center, ask the user whether they accept the method of sending the product for repair.
Tip: If the user has any dissatisfaction with the inquiry about repair center, use the action 「Search Knowledge」 to provide professional knowledge for reassurance. - Knowledge Base Scope: Store and repair center knowledge base.
- End Condition: The current LLM node ends when the customer clearly indicates that they want to go to a specific repair center.
# Feature Description
- Define Your Task Workflow: Define the current process based on your business requirements and break it down into multiple subtasks.
- Define Subtasks: Configure the LLM Task Node and set up your subtasks.
a. Task Objective: Define the goal that the current node needs to achieve.
b. Task Steps: Define how the LLM of this node executes the task. When writing prompts for task steps, you can reference actions and variables, which will prompt the LLM to call external interfaces or store data at the appropriate time.
● Referencing Variables: If data needs to be transferred between different LLM Task Nodes, implement the reference through variables in the task steps. Examples:
i. Reading variables: Read the variable 「Order Status」. If the status is "Shipped", perform the corresponding operation; if not shipped, directly modify the address.
ii. Storing variables: Store the value of the interface return parameter "orderid" in the variable 「Order Number」.
● Referencing Actions:
i. You can directly reference actions that have been created in "Knowledge Center - Action Management".
ii. Writing example: Collect the user's located city and use the action 「Search Repair Center」 to check whether there are suitable repair center in the local area.
● Using Interface Parameters:
i. If a parameter is only used within the current LLM Task Node and does not need to be stored as a variable, you can directly reference the parameter name in the prompt.
ii. Writing example: Use the interface return parameter "orderid" to call the action 「Inquire About Logistics」 to obtain the user's logistics progress information.
c. Knowledge Base Scope: When a knowledge-related question is identified, the LLM Task Node will call the knowledge base to provide an answer. You can define the scope for knowledge base queries. If you proactively reference the "Search Knowledge" action in the task steps, the LLM will be guided to query the knowledge base directly, and the query scope will also be within the configured knowledge base range.
d. End Condition: You can customize the termination condition. For example, "when the customer confirms that the problem has been resolved", the current LLM Task Node will terminate, and the process will follow the branch to the next node. The task will also be forced to terminate when the maximum number of conversation rounds is exceeded. - Connect LLM Task Nodes with Other Nodes
- Test the AI Agent Performance