Webpage Knowledge
# Webpage Knowledge
——Learn how to use the webpage knowledge we provide for you and its application scenarios through this article.
# The Role of Webpage Knowledge
We hope that before you learn about the webpage knowledge function, you can understand its scenarios and uses:
● Use scenario: A large amount of enterprise knowledge is stored on public web pages. It needs to be quickly transferred into the knowledge base through a low-cost method, and it also needs to support the synchronization capability for web page updates.
● Purpose: The knowledge center supports syncing knowledge from websites directly via URL. You need to provide the public URL here, and we will follow the robot.txt protocol to obtain the webpage content.
# How to Create and Set up Web Knowledge:
On the [Knowledge Base Management] page, click the [Create] button to establish a web knowledge base.
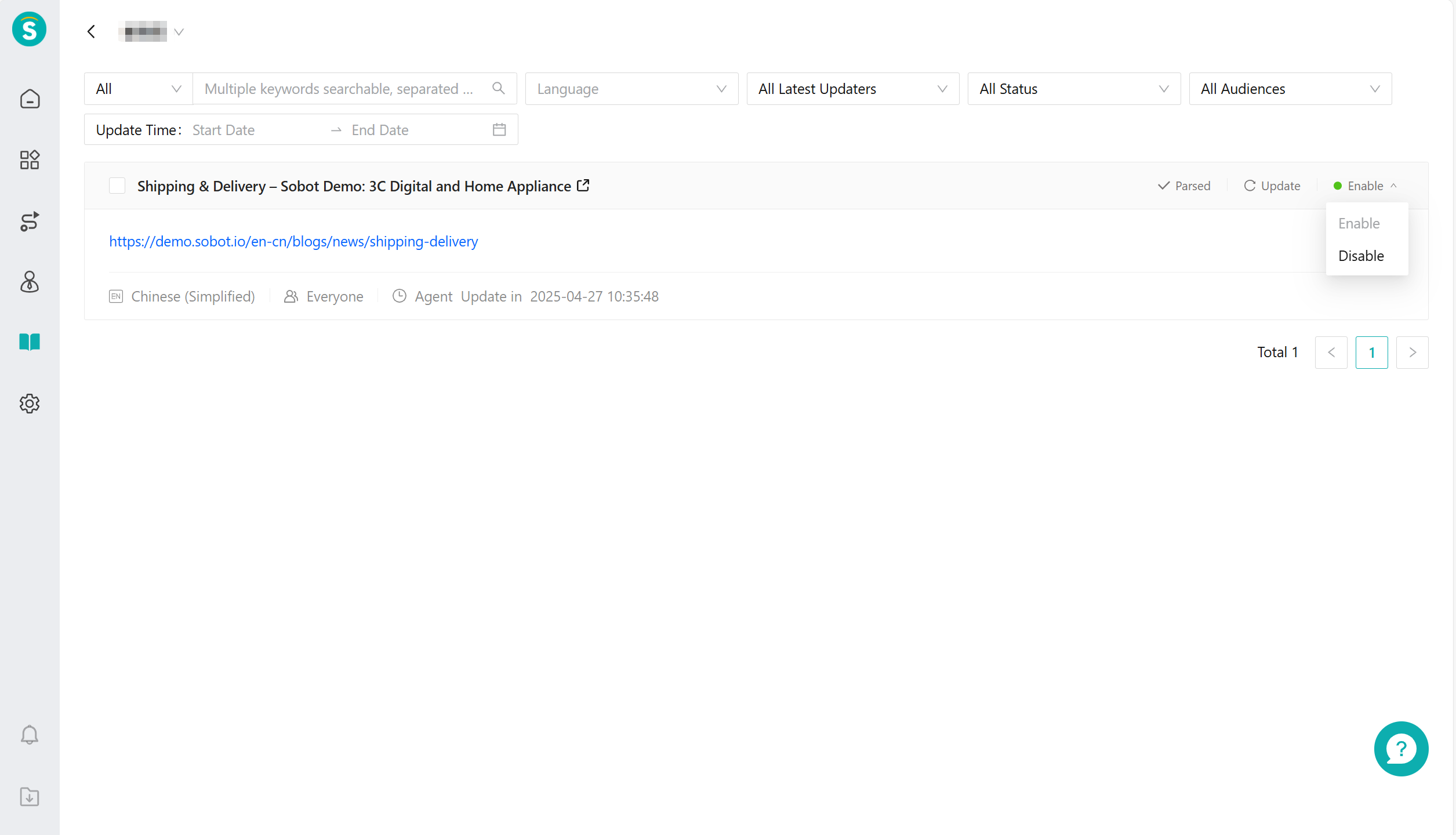
Edit Knowledge Base: Filter and set up the knowledge base.
Update Knowledge Base: Supports synchronized updates for the entire URL; During the knowledge update process, it will be invalid. To avoid affecting the use of large model robots, it is recommended not to update during peak customer consultation hours.
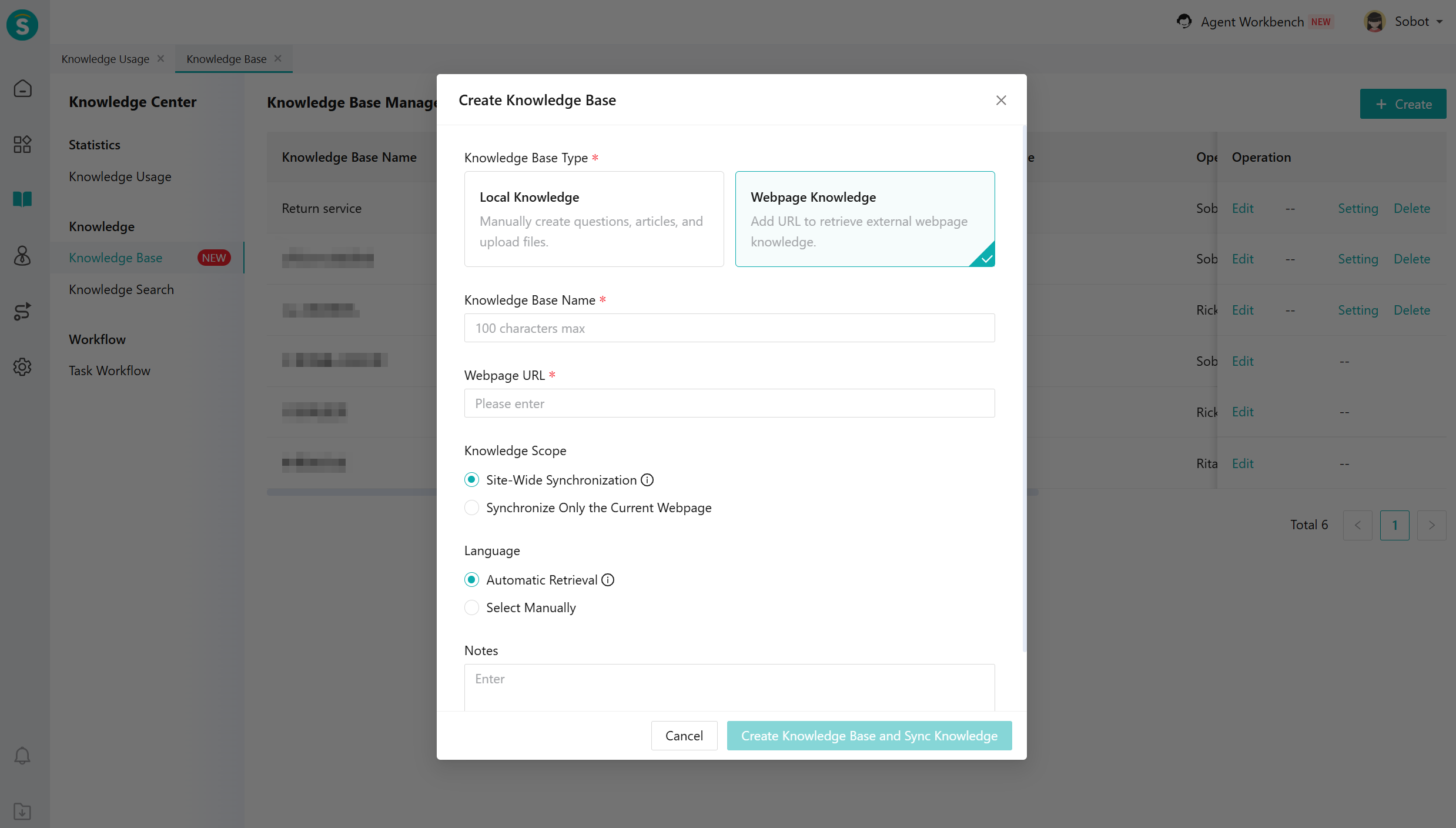
# Layered Deep Search & Search from Sitemap
Currently, the entire site supports two synchronization modes, and you can choose based on your actual needs.
| Type | Search from Sitemap | Layered Deep Search |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Crawls webpages based on the sitemap provided by the website | Retrieves all URLs from the first-level webpage and drills down to crawl, then continues to retrieve all URLs from the second level and drills down further, crawling layer by layer |
| Advantages | Allows limiting the scope of webpage retrieval | Suitable for the vast majority of webpages |
| Disadvantages | Incomplete sitemap maintenance may result in incomplete webpage retrieval | Unable to limit the scope of webpage retrieval, which may synchronize some webpages that are less important for enterprise customers |
# Explanation of Webpage Synchronization Failures
If you encounter webpage synchronization failures, please follow the troubleshooting steps below to identify the cause:
Check if the robots.txt file exists under the website:
a. When the website does not have a robots.txt file, it is considered that the website has not authorized third-party crawlers, and "Webpage content forbidden to access" will be returned. To check if a robots.txt file exists under the website, you can query the website's robots.txt file by adding /robots.txt after the root directory of the website. For example, the robots.txt file of a webpage can be queried this way. For more information about robots.txt, you can refer to the official Google documentation.https://developers.google.com/search/docs/crawling-indexing/robots/robots_txt (opens new window)
b. If the query result is empty, you need to add a robots.txt file for the website. You can refer to the following method for adding it.https://developers.google.com/s earch/docs/crawling-indexing/robots/create-robots-txt (opens new window)
Check the User-Agent, Disallow, and Allow fields in the website's robots.txt file: These three fields define the scope of web crawling for crawler tools. If the webpage you entered is within the Disallow path, it will return "Content blocked from being fetched" (Disallow: / means all pages cannot be crawled). If the webpage you entered is within the Disallow path, modify the content of the robots.txt protocol, for example, change it to Allow: /.
When using Site-wide Sync with Sitemap, check the website's sitemap file:
a. In full-site synchronization mode, Sobot currently uses the subpages in the sitemap of the website's robots.txt as synchronization targets. For more information about sitemaps, you can refer to the introduction in Google's official documentation: . If the robots.txt does not contain a sitemap file, it will return "Webpage content forbidden to be fetched." In this case, we recommend that you add a sitemap file for your website.https://developers.google.com/search/d ocs/crawling-indexing/sitemaps/overview (opens new window)
b. When obtaining sub-pages from the sitemap, we will filter out pages with a URL path matching your input and synchronize their content (for example, when you input a specific path, corresponding pages such as will be filtered, while unrelated pages like will not be synchronized). If the sitemap does not contain pages matching the URL path you entered, the system will return "Content retrieval prohibited for this page." In this case, it is recommended to input the top-level domain when synchronizing pages across the entire site, or to supplement and improve the website's sitemap.www.example.com/product (opens new window)www.example.com/product/129330 (opens new window)www.example.com/helpcenter (opens new window)
Single Webpage Sync Failure
a. Check if the webpage can be opened normally: Verify whether the webpage loads properly in a browser. If the webpage is abnormal, crawling cannot proceed.
b. Try "Resync": Some webpages might experience connection timeouts during crawling. Attempting to resync may result in successful synchronization.
